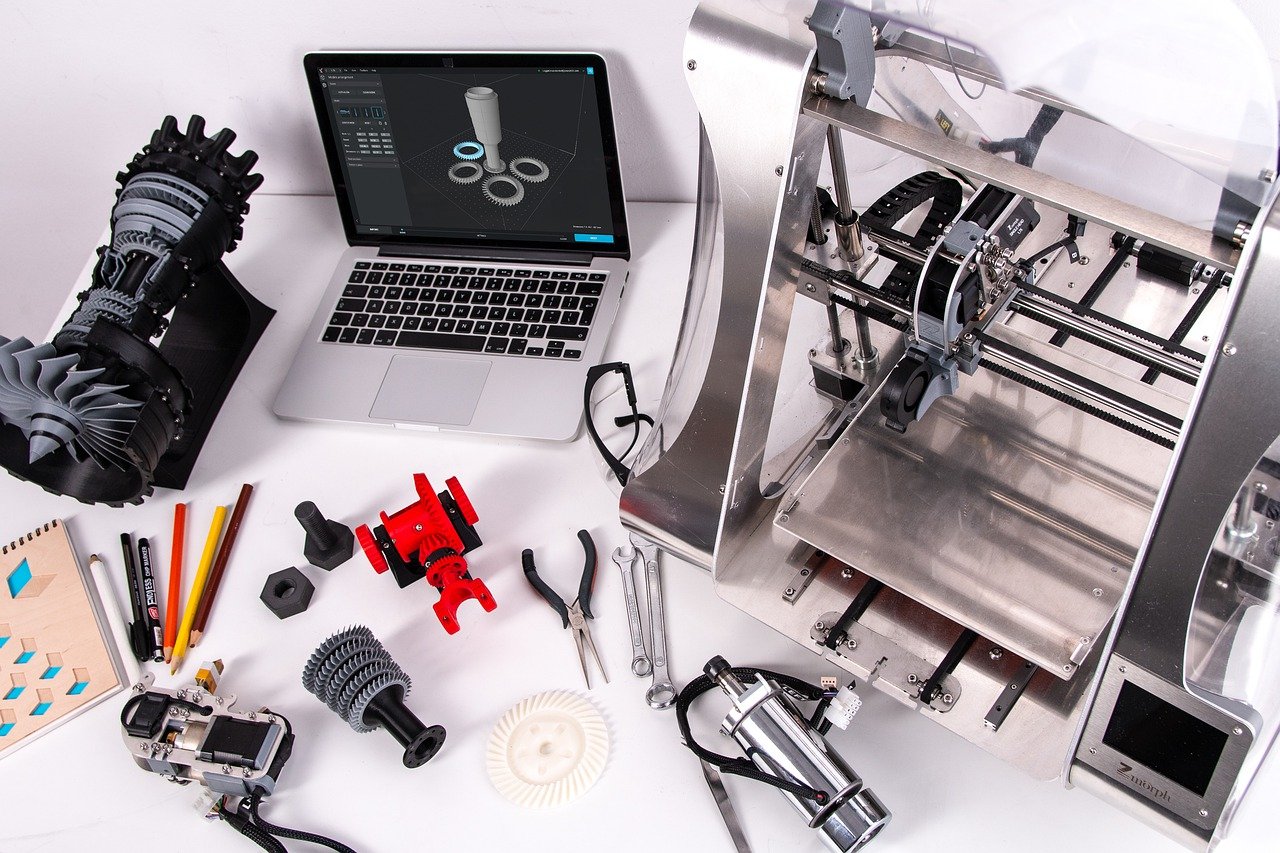
Additive manufacturing, or 3D printing, isn’t the future anymore. It’s here now. And it’s gaining ground steadily against traditional manufacturing. 3D printing is now found in tool and die production, custom implants, pilot line manufacturing, and mass production.
Additive manufacturing allows manufacturers to build complex parts quickly and cost-effectively—all while boosting part quality. This approach saves on material waste/energy, reduces the need for carrying much on-hand inventory, and simplifies and optimizes legacy part production, to name a few of its benefits.
3D printing encompasses several different manufacturing processes. These fall into two basic categories—direct deposit and bulk deposit processes. Some processes within these categories require thermal processing post-production technologies to achieve the desired physical characteristics, mechanical properties, and/or print quality a company wants.
Unleashing the Power of Post-Production Processing
While the inherent advantages of 3D printing are undeniable, the quest for perfection often extends beyond the printing stage. Post-production processing emerges as a crucial phase in refining the properties and aesthetics of printed objects. This is where industrial ovens emerge as indispensable tools, offering a gateway to enhanced performance and functionality.
The Role of Industrial Ovens in Post-Production Enhancement
Industrial ovens serve as the linchpin of post-production thermal processing, providing a controlled environment for tempering and annealing 3D printed components. By subjecting printed parts to carefully calibrated temperature profiles, manufacturers can fine-tune material properties, optimize mechanical strength, and eliminate residual stresses, thereby elevating the overall quality of the end product.
Below are three use cases of manufacturers using industrial ovens to alter the quality and/or properties of 3D prints during post-production:
- Annealing is a little-known but viable post-production process when it comes to producing high-quality 3D prints. Annealing uses heat to modify the properties of metal and plastic 3D parts to produce different desired properties, including increased hardness, impact resistance, softening, and increased ductility.
In this use case, the manufacturer employs an industrial oven to heat 3D plastic prints to their “glass transition temperature.” The object retains its shape at this temperature but softens. Ongoing changes on the molecular level boost the print’s structure stability. - Curing is another thermal process technology that can change the physical properties of 3D prints. Curing toughens or hardens a polymer material by the crosslinking of polymer chains.
One manufacturer leverages 3D printing to produce products comprised of a production grade-elastomer. Curing these parts in an industrial oven enables the manufacturer to produce a product with variable properties—an approach that serves as an alternative to injection and compression molding. - Curing is also well-suited to changing 3D prints’ properties to ready a part for a second production phase. In this use case, the manufacturer uses thermal processing to crosslink the printed metal parts inside a build box at specific temperatures.
This step provides enough strength to allow part handling for de-powdering the print. The manufacturer then loads the powdered metal into the oven for thermal de-binding, which removes the residual binder material from the metal parts before sintering.
These are just three examples of the increasingly innovative ways manufacturers are using industrial ovens in 3D post-production. Savvy manufacturers will continue to find new ways of combining thermal processing with help from industrial ovens and 3D printing as time passes.
A Multifaceted Approach to Quality Enhancement
The applications of industrial ovens in 3D printing are multifaceted, encompassing a spectrum of post-production techniques tailored to specific material requirements and performance objectives. From annealing to curing, each process harnesses the transformative power of heat to unlock latent potential and imbue printed parts with superior characteristics.
Driving Innovation through Thermal Processing
The marriage of industrial ovens and 3D printing heralds a new era of innovation, enabling manufacturers to push the boundaries of what is possible. Whether it’s optimizing material properties for demanding applications or refining surface finishes for aesthetic appeal, the synergy between thermal processing and additive manufacturing paves the way for limitless creativity and ingenuity.
Embracing the Future of Manufacturing
As additive manufacturing continues its relentless march towards ubiquity, the role of industrial ovens in shaping its trajectory cannot be overstated. By embracing advanced thermal processing techniques, manufacturers can unleash the full potential of 3D printing, driving efficiency, scalability, and sustainability across diverse industries.
Conclusion: A Path Towards Excellence
In the dynamic landscape of modern manufacturing, excellence is not merely an aspiration but a prerequisite for success. By harnessing the transformative power of industrial ovens, manufacturers can embark on a journey towards unparalleled quality, innovation, and competitiveness in the digital age.